The American Academy of Dermatology provides resources to find a Dermatologist in your area!
Stop CancerToday
Skin cancer, including melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma, is highly treatable when caught early. Regular checks, especially if you’re at higher risk (fair skin, history of sunburns, family history), can save lives.
Lives Saved
10K
SPF
30+
Key PreventionMethods
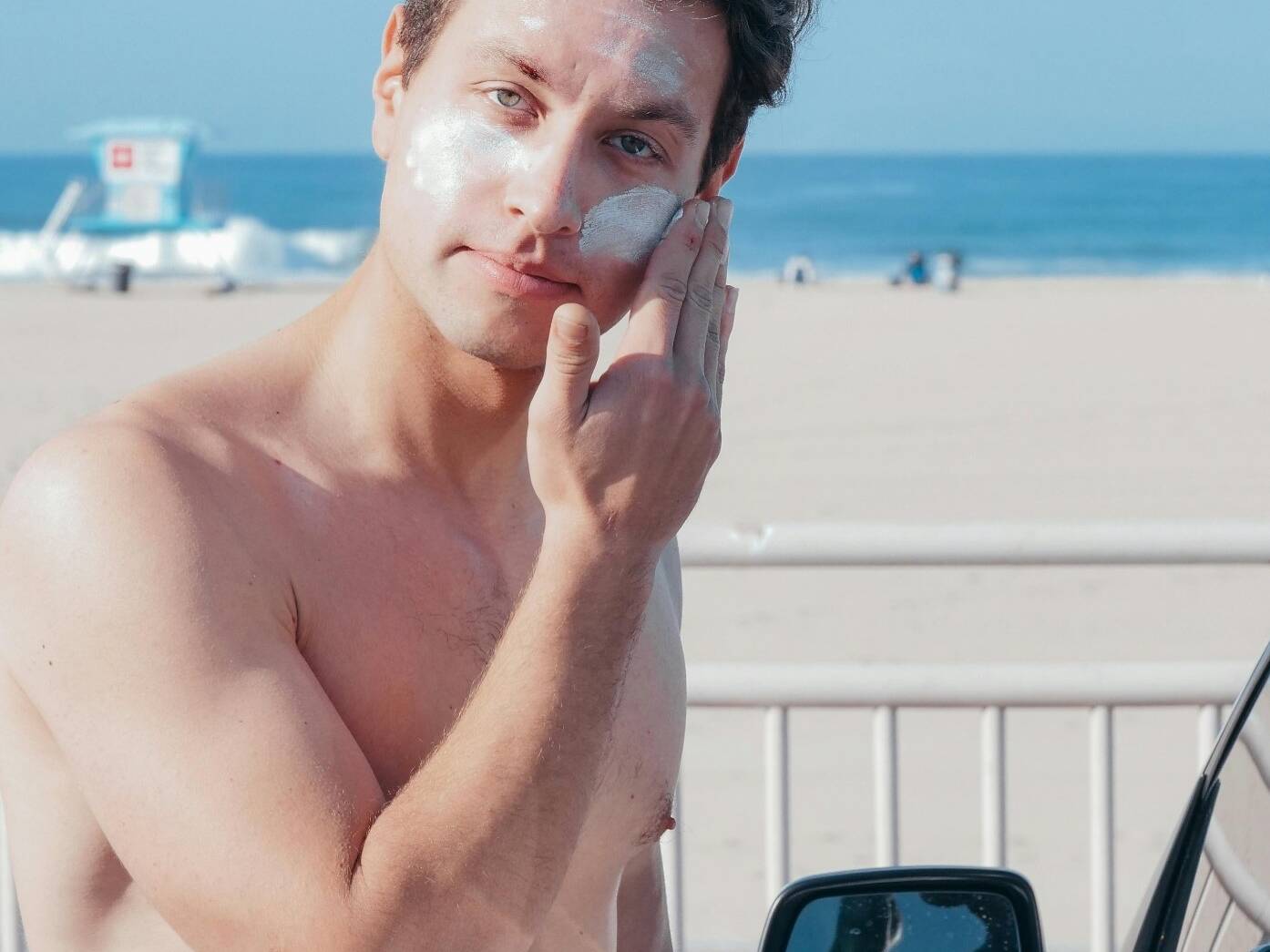
Regular use of broad-spectrum sunscreen
Avoid ExcessiveSun Exposure
Avoiding tanning beds and excessive sun exposure.
Exposure Time
10-4PM
Golfers
27%
Too ManyGolfers
27% of golfers had a history of skin cancer, compared to 7% of the general public, indicating a nearly 250% greater risk for golfers.
Need to know
Here are the most frequently asked questions (FAQ) about melanoma and skin cancer:
Skin cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. It commonly develops on areas exposed to the sun but can occur anywhere on the body.
- Melanoma: The most dangerous, can spread to other organs if not caught early.
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC): Most common, slow-growing, rarely spreads.
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): Second most common, can spread if untreated.
The primary cause is overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds. Other factors include genetics, skin type, and a history of sunburns.
People with fair skin, light eyes, and hair, a history of sunburns, or a family history of skin cancer are at higher risk. Anyone can get skin cancer, regardless of YOUR skin tone.
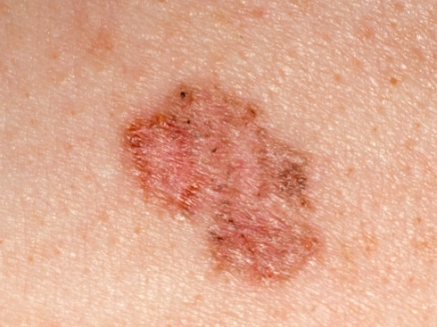
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that begins in melanocytes (pigment-producing cells). It is less common but more likely to spread and become life-threatening.
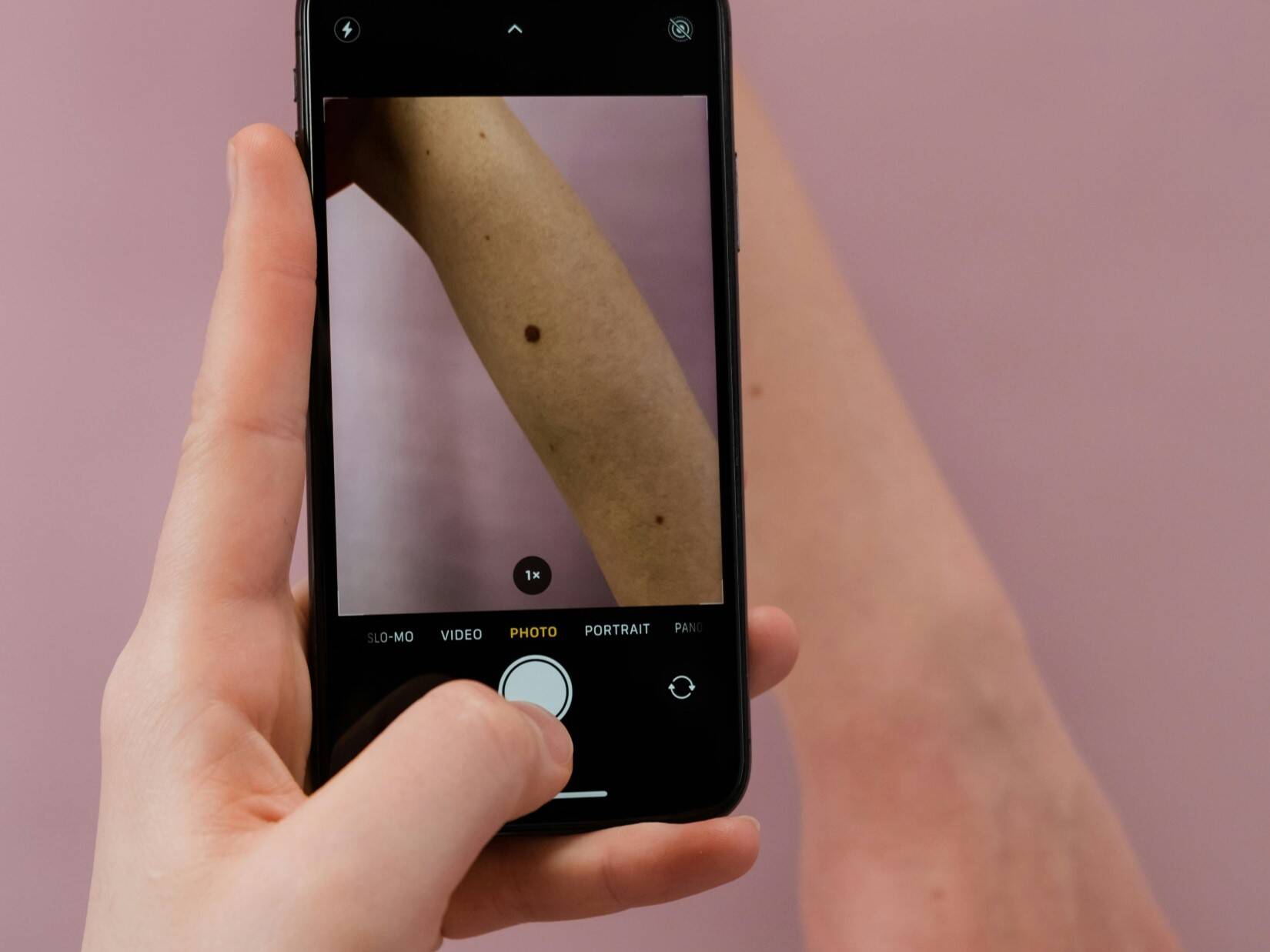
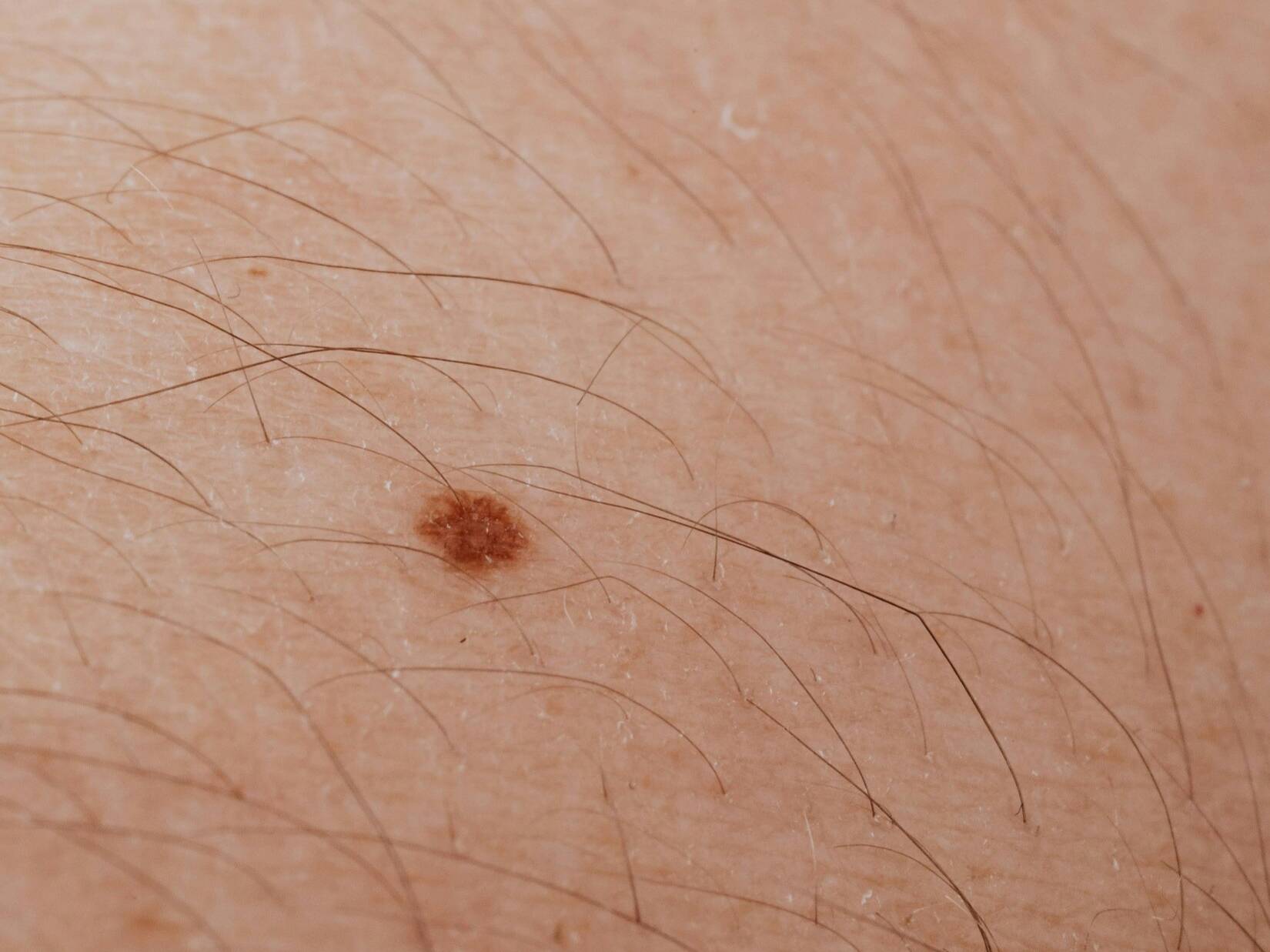
It often appears as a new, unusual mole or a change in an existing mole. Use the ABCDE rule to identify potential melanoma:
- Asymmetry
- Border irregularity
- Color variation
- Diameter (larger than 6mm)
- Evolving (changing in size, shape, or color)
Yes, when detected early, melanoma is highly treatable. Advanced melanoma is harder to treat but new therapies, like immunotherapy, have improved outcomes.
You can also monitor your skin with the ABCDE Rule:
Asymmetry – one half of a mole doesn’t match the other. Border – irregular, blurred, or jagged edges. Color – uneven colors or multiple shades. Diameter – larger than a pencil eraser. Evolving – changing size, shape, or color.
- MelanomaEarly detection and prevention can reduce melanoma mortality by 20-50%, potentially saving 4,000–10,000 lives annually in the U.S. alone.
- Non-Melanoma Skin CancersPreventative measures like sunscreen use and early treatment avoid the progression of millions of cases, significantly lowering healthcare burdens and saving lives indirectly.
- Broad ImpactPublic health campaigns promoting sun safety, sunscreen, and regular skin checks are estimated to save 10,000+ lives worldwide annually, particularly in high-risk regions like Australia and the U.S.
- Key prevention methods include:Prevention includes using a wide brimmed hat, golf sleeves, regular use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher. We recommend a mineral base sunscreen with a SPF of 30. Avoiding tanning beds and excessive sun exposure, especially between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m. Wearing protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses. Conducting self-skin exams and seeking professional screenings.